Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Beijing Institute for Advanced Study, National University of Defense Technology, Beijing 100020, China
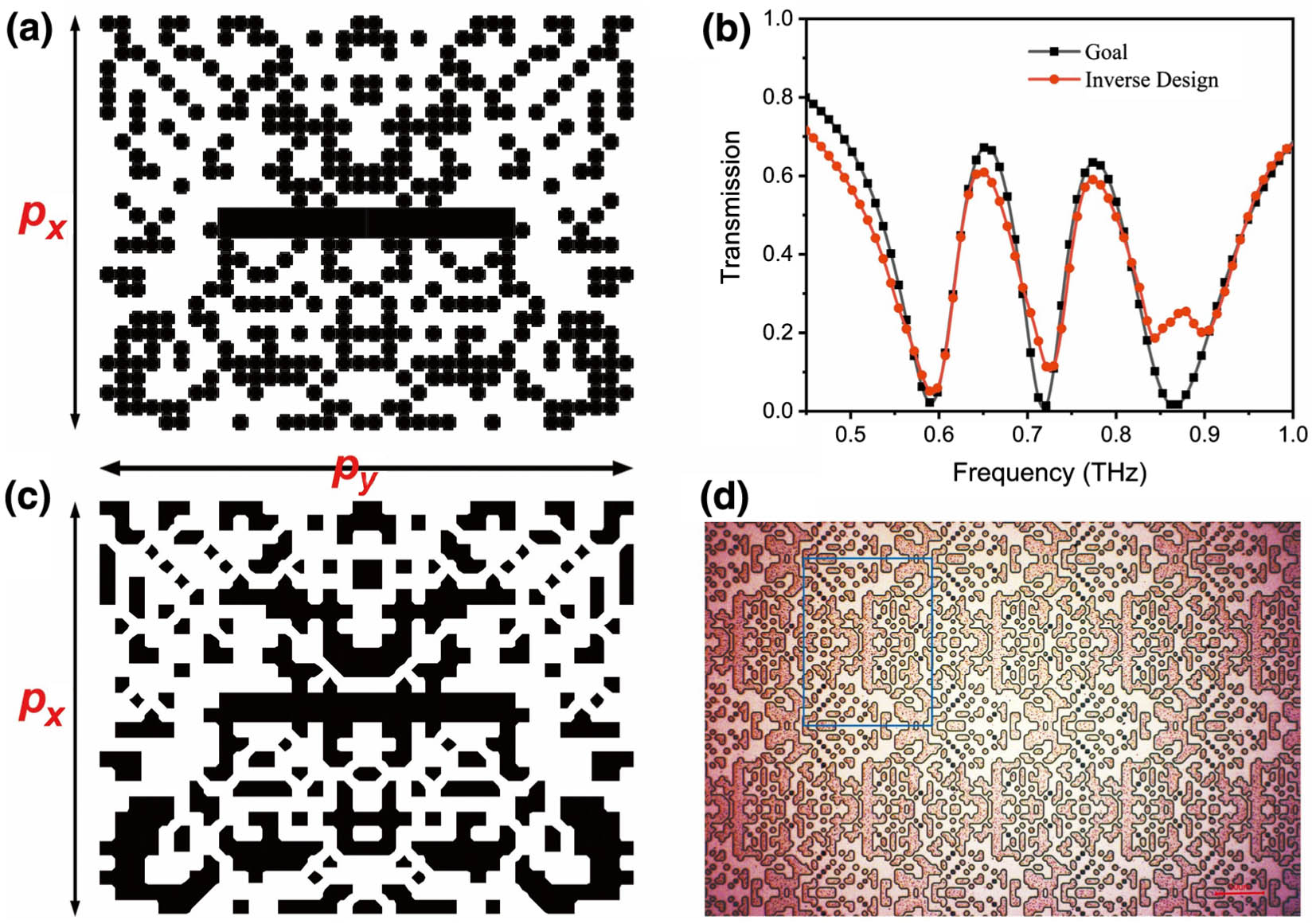
Terahertz metasurfaces have great applications for efficient terahertz modulation, but there are still problems in designing terahertz metadevices in terms of complexity and inefficiency. Herein, we demonstrate an inversely-designed terahertz metasurface with double electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like windows by incorporating a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. We prepared and tested the metadevices, and the experimental terahertz signals are close to the designed results. By hybridizing amorphous germanium film with the inversely-designed metasurface, two EIT-like windows, including transmission and slow-light effect, exhibit ultrafast modulation behavior in 25 ps excited by a femtosecond laser. The modulation depths of transmission in two transparency windows are 74% and 65%, respectively. The numerical simulations also illustrate the ultrafast dynamic process and modulation mechanism, which match well with the experiment results. Our work thus offers opportunities for designing other objective functions of the terahertz metadevice.
terahertz metasurfaces inverse design double electromagnetically induced transparency Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(11): 113701
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(1): 011010
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology, Hefei 230037, China
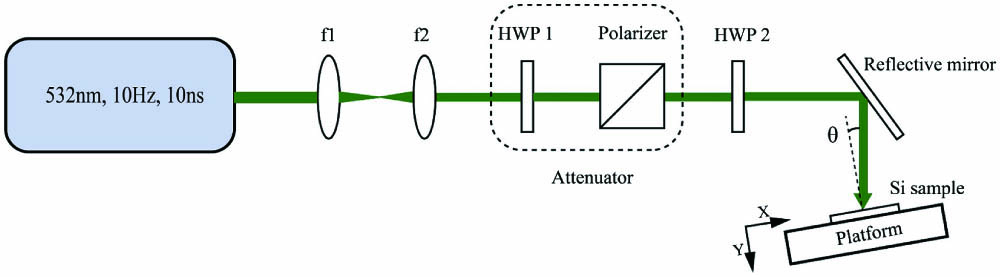
In this paper, an effective method is proposed to generate specific periodical surface structures. A 532 nm linearly polarized laser is used to irradiate the silicon with pulse duration of 10 ns and repetition frequency of 10 Hz. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs) are observed when the fluence is and the number of pulses is 1000. The threshold of fluence for generating LIPSS gradually increases with the decrease of the number of pulses. In addition, the laser incident angle has a notable effect on the period of LIPSS, which varies from 430 nm to 1578 nm, as the incident angle ranges from 10° to 60° correspondingly. Besides, the reflectivity is reduced significantly on silicon with LIPSS.
laser-induced periodic surface structure nanostructures fluence number of pulses incident angle Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(1): 013802

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Beijing Institute for Advanced Study, National University of Defense Technology, Beijing 100020, China
Metasurface plays a key role in various terahertz metadevices, while the designed terahertz metasurface still lacks flexibility and variety. On the other hand, inverse design has drawn plenty of attention due to its flexibility and robustness in the application of photonics. This provides an excellent opportunity for metasurface design as well as the development of multifunctional, high-performance terahertz devices. In this work, we demonstrate that, for the first time, a terahertz metasurface supported by the electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) effect can be constructed by inverse design, which combines the particle swarm optimization algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. Incorporating germanium (Ge) film with inverse-designed metasurface, an ultrafast EIT modulation on the picosecond scale has been experimentally verified. The experimental results suggest a feasibility to build the terahertz EIT effect in the metasurface through an optimization algorithm of inverse design. Furthermore, this method can be further utilized to design multifunctional and high-performance terahertz devices, which is hard to accomplish in a traditional metamaterial structure. In a word, our method not only provides a novel way to design an ultrafast all-optical terahertz modulator based on artificial metamaterials but also shows the potential applications of inverse design on the terahertz devices.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(6): 06001099

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences China, Beijing 100071, China
3 Shenzhen Engineering Laboratory of Phosphorene and Optoelectronics and Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 e-mail: hzhang@szu.edu.cn
The year 2019 marks the 10th anniversary of the first report of ultrafast fiber laser mode-locked by graphene. This result has had an important impact on ultrafast laser optics and continues to offer new horizons. Herein, we mainly review the linear and nonlinear photonic properties of two-dimensional (2D) materials, as well as their nonlinear applications in efficient passive mode-locking devices and ultrafast fiber lasers. Initial works and significant progress in this field, as well as new insights and challenges of 2D materials for ultrafast fiber lasers, are reviewed and analyzed.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(1): 01000078
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100010, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Laser Interaction with Matter, Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi’an 710024, China
Standing on the potential for high-speed modulation and switching in the terahertz (THz) regime, all-optical approaches whose response speeds mainly depend on the lifetime of nonequilibrium free carriers have attracted a tremendous attention. Here, we establish a novel bi-direction THz modulation experiment controlled by femtosecond laser for new functional devices. Specifically, time-resolved transmission measurements are conducted on a series of thin layers Bi2Se3 films fabricated straightforwardly on Al2O3 substrates, with the pump fluence range from 25 μJ/cm2 to 200 μJ/cm2 per pulse. After photoexcitation, an ultrafast switching of THz wave with a full recovery time of ~10 ps is observed. For a longer timescale, a photoinduced increase in the transmitted THz amplitude is found in the 8 and 10 quintuple layers (QL) Bi2Se3, which shows a thickness-dependent topological phase transition. Additionally, the broadband modulation effect of the 8 QL Bi2Se3 film is presented at the time delays of 2.2 ps and 12.5 ps which have a maximum modulation depth of 6.4% and 1.3% under the pump fluence of 200 μJ/cm2, respectively. Furthermore, the absorption of α optical phonon at 1.9 THz shows a time-dependent evolution which is consistent with the cooling of lattice temperature.
Ultrafast optics topological insulator ultrafast photonic devices Photonic Sensors
2019, 9(3): 268
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100071, China
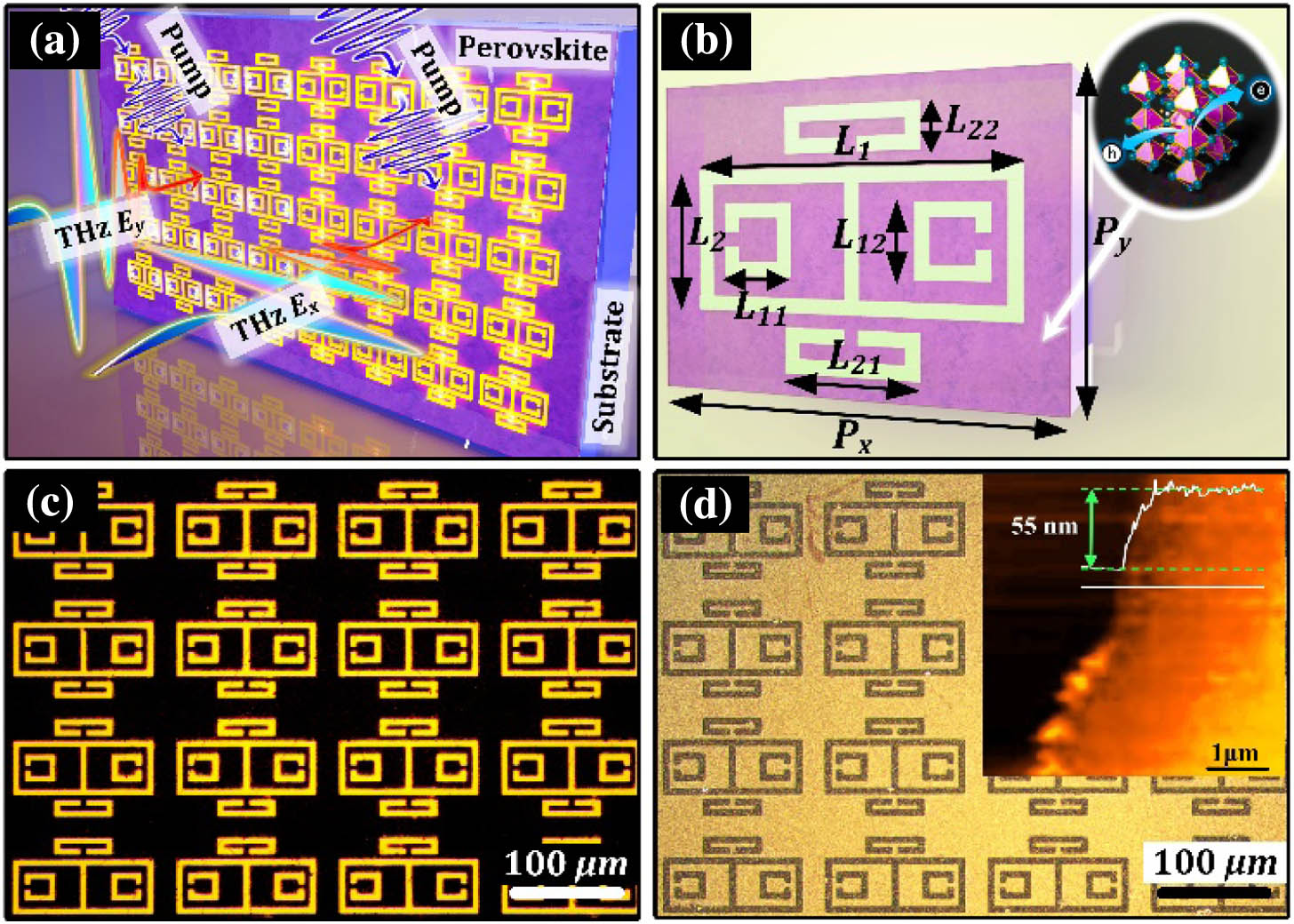
Active control of metamaterial properties with high tunability of both resonant intensity and frequency is essential for advanced terahertz (THz) applications, ranging from spectroscopy and sensing to communications. Among varied metamaterials, plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) has enabled active control with giant sensitivity by embedding semiconducting materials. However, there is still a stringent challenge to achieve dynamic responses in both intensity and frequency modulation. Here, an anisotropic THz active metamaterial device with an ultrasensitive modulation feature is proposed and experimentally studied. A radiative-radiative-coupled PIT system is established, with a frequency shift of 0.26 THz in its sharp transparent windows by polarization rotation. Enabled by high charge-carrier mobility and longer diffusion lengths, we utilize a straightforwardly spin-coated film acting as a photoactive medium to endow the device with high sensitivity and ultrafast speed. When the device is pumped by an ultralow laser fluence, the PIT transmission windows at 0.86 and 1.12 THz demonstrate a significant reduction for two polarizations, respectively, with a full recovery time of 561 ps. In addition, we numerically prove the validity that the investigated resonator structure is sensitive to the optically induced conductivity. The hybrid system not only achieves resonant intensity and frequency modulations simultaneously, but also preserves the all-optical-induced switching merits with high sensitivity and speed, which enriches multifunctional subwavelength metamaterial devices at THz frequencies.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(9): 09000994
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Interdisciplinary Center of Quantum Information, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4 National Institute of Defense Technology Innovation, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100010, China
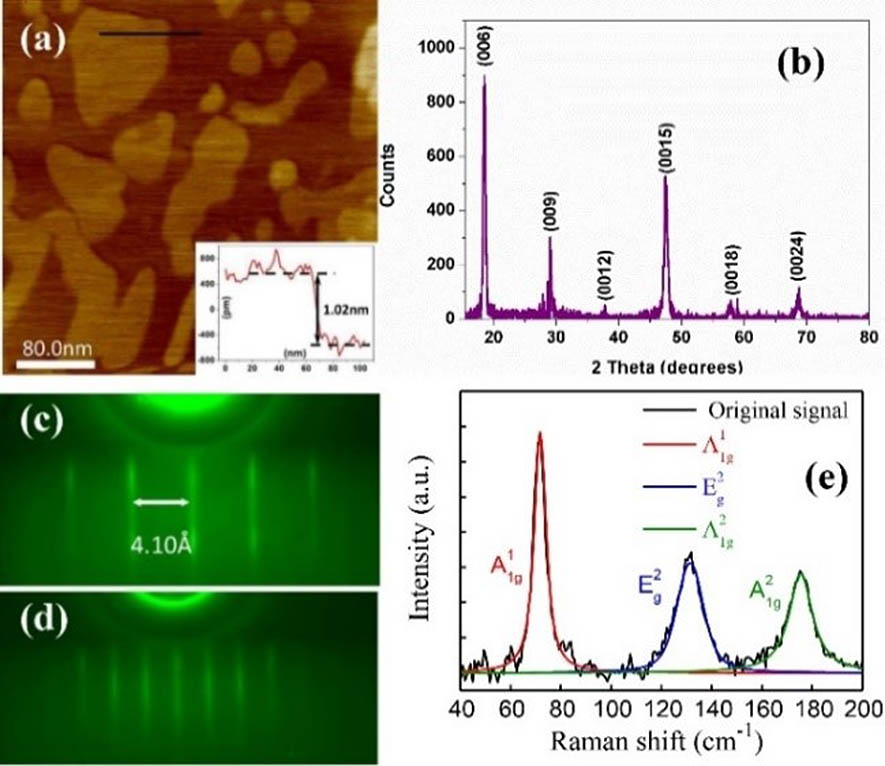
Broadband transient reflectivity traces were measured for Bi2Se3 thin films with various substrates via a 400 nm pump–white-light-probe setup. We have verified the existence of a second Dirac surface state in Bi2Se3 and qualitatively located it by properly analyzing the traces acquired at different probe wavelengths. Referring to the band structure of Bi2Se3, the relaxation mechanisms for photo-excited electrons with different energies are also revealed and studied. Our results show a second rise of the transient reflection signal at the time scale of several picoseconds. The types of substrate can also significantly affect the dynamics of the rising signal. This phenomenon is attributed to the effect of lattice heating and coherent phonon processes. The mechanism study in this work will benefit the fabrication of high-performance photonic devices based on topological insulators.
160.4236 Nanomaterials 300.6500 Spectroscopy, time-resolved Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020005
1 国防科学技术大学 光电科学与工程学院, 长沙 410073
2 光电信息控制和安全技术重点实验室, 河北 三河 065201
用1064nm皮秒脉冲激光辐照PV型线阵HgCdTe探测器,随着激光能量的增大,探测单元出现了不同程度的损伤,发现了致损单元的反常响应现象,致损单元响区蓝移,对波长为1064nm的光响应灵敏度明显增强。结果表明:受损单元p型碲镉汞层出现汞析出现象后,受损光敏元碲镉汞材料组分和载流子浓度发生变化,pn结耗尽层宽度的变化导致pn结等效电阻变化,这是导致芯片损伤单元出现反常响应的主要因素。研究发现受损光敏元随着碲镉汞材料组分增大,碲镉汞材料能带禁带宽度增大,使探测器响区出现蓝移现象,这是损伤单元对波长为1064nm激光响应更加灵敏的主要原因。
HgCdTe线阵探测器 激光 反常响应 耗尽层电阻 响区蓝移 禁带宽度 HgCdTe linear array detector laser abnormal response depletion layer resistance response range blue shift band gap width
国防科学技术大学光电科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
在红外成像系统中,串扰会降低图像的清晰度,影响焦平面阵列的分辨率性能和成像质量,因此对串扰的测试及产生机理等研究至关重要。对比了串扰效应的3 种测试原理和测试方法,从光学串扰和电学串扰两个方面揭示了串扰效应的产生机理,综述了两种串扰类型的解决方案,并对未来红外成像器件的发展趋势进行展望,以期为改进相关器件的技术、结构和制造工艺提供有益的借鉴。
成像系统 红外 串扰 光学串扰 电学串扰 激光与光电子学进展
2015, 52(10): 100004





